VBA – Cómo Utilizar las Funciones de Hoja de Cálculo (y una Lista Completa)
In this Article
Hay muchas maneras de utilizar funciones en VBA. VBA viene cargado con muchas funciones incorporadas. Incluso puede crear sus propias funciones (UDFs). Sin embargo, también puede utilizar muchas de las funciones de Excel en VBA utilizando Application.WorksheetFunction.
Cómo Utilizar Funciones de Hoja de Cálculo en VBA
Para acceder a una función de Excel en VBA añada Application.WorksheetFunction delante de la función que desea llamar. En el siguiente ejemplo, llamaremos a la Función Max de Excel:
Dim maxvalue as long
maxvalue = Application.WorksheetFunction.Max(Range("A1").Value, Range("A2").Value)La sintaxis de las funciones es la misma, sin embargo usted ingresará los argumentos de la función tal como lo haría con cualquier otra función VBA.
Note que la sintaxis de la Función Max aparece cuando usted escribe (similar a las Funciones VBA):

Método WorksheetFunction
WorksheetFunction es un método del objeto Application. Le permite acceder a muchas (no todas) de las funciones estándar de la hoja de cálculo de Excel. Generalmente, no tendrás acceso a ninguna función de hoja de cálculo que tenga su correspondiente versión VBA.
A continuación puede ver una lista de muchas de las Funciones de Hoja de Cálculo más comunes.
Application.WorksheetFunction vs. Application
En realidad hay dos formas de acceder a estas funciones: Application.WorksheetFunction (como se ve arriba):
maxvalue = Application.WorksheetFunction.Max(Range("a1").Value, Range("a2").Value)o puede omitir WorksheetFunction
maxvalue = Application.Max(Range("a1").Value, Range("a2").Value)Desafortunadamente, omitir la WorksheetFunction eliminará el Intellisense que muestra la sintaxis (ver imagen anterior). Sin embargo, tiene una gran ventaja potencial: Manejo de Errores.
Si utiliza Application, y su función genera un error devolverá el valor del error. Si utiliza el método WorksheetFunction, VBA arrojará un error en tiempo de ejecución. Por supuesto, usted puede manejar el error de VBA, pero generalmente es mejor evitar el error en primer lugar. Veamos un ejemplo para ver la diferencia:
Manejo de Errores de la Función de Hoja de Cálculo Vlookup
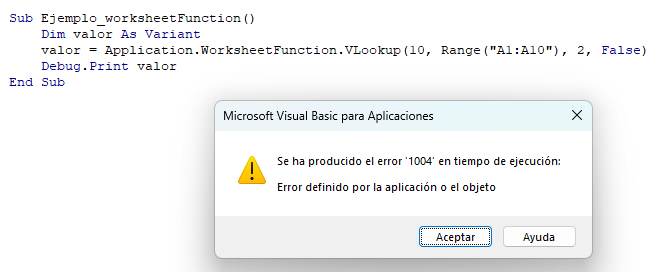
Intentaremos realizar un Vlookup que no resultará en una coincidencia. Por lo tanto, la función Vlookup devolverá un error.
Primero, utilizaremos el método WorksheetFunction. Observe como VBA arroja un error:
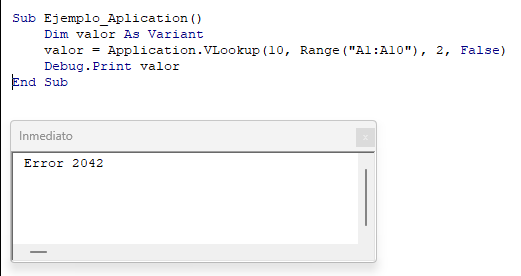
A continuación omitimos WorksheetFunction. Observe cómo
A continuación omitiremos la función WorksheetFunction. Observe como no se lanza ningún error y en su lugar la función ‘valor’ contiene el valor de error del Vlookup.
Lista de Funciones de Hoja de Cálculo VBA
A continuación encontrará una lista de la mayoría de los comunes VBA WorksheetFunctions.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Logical | |
| AND | Checks whether all conditions are met. TRUE/FALSE |
| IF | If condition is met, do something, if not, do something else. |
| IFERROR | If result is an error then do something else. |
| OR | Checks whether any conditions are met. TRUE/FALSE |
| Lookup & Reference | |
| CHOOSE | Chooses a value from a list based on it's position number. |
| HLOOKUP | Lookup a value in the first row and return a value. |
| INDEX | Returns a value based on it's column and row numbers. |
| LOOKUP | Looks up values either horizontally or vertically. |
| MATCH | Searches for a value in a list and returns its position. |
| TRANSPOSE | Flips the oriention of a range of cells. |
| VLOOKUP | Lookup a value in the first column and return a value. |
| Date & Time | |
| DATE | Returns a date from year, month, and day. |
| DATEVALUE | Converts a date stored as text into a valid date |
| DAY | Returns the day as a number (1-31). |
| DAYS360 | Returns days between 2 dates in a 360 day year. |
| EDATE | Returns a date, n months away from a start date. |
| EOMONTH | Returns the last day of the month, n months away date. |
| HOUR | Returns the hour as a number (0-23). |
| MINUTE | Returns the minute as a number (0-59). |
| MONTH | Returns the month as a number (1-12). |
| NETWORKDAYS | Number of working days between 2 dates. |
| NETWORKDAYS.INTL | Working days between 2 dates, custom weekends. |
| NOW | Returns the current date and time. |
| SECOND | Returns the second as a number (0-59) |
| TIME | Returns the time from a hour, minute, and second. |
| TIMEVALUE | Converts a time stored as text into a valid time. |
| WEEKDAY | Returns the day of the week as a number (1-7). |
| WEEKNUM | Returns the week number in a year (1-52). |
| WORKDAY | The date n working days from a date. |
| YEAR | Returns the year. |
| YEARFRAC | Returns the fraction of a year between 2 dates. |
| Engineering | |
| CONVERT | Convert number from one unit to another. |
| Financial | |
| FV | Calculates the future value. |
| PV | Calculates the present value. |
| NPER | Calculates the total number of payment periods. |
| PMT | Calculates the payment amount. |
| RATE | Calculates the interest Rate. |
| NPV | Calculates the net present value. |
| IRR | The internal rate of return for a set of periodic CFs. |
| XIRR | The internal rate of return for a set of non-periodic CFs. |
| PRICE | Calculates the price of a bond. |
| INTRATE | The interest rate of a fully invested security. |
| Information | |
| ISERR | Test if cell value is an error, ignores #N/A. TRUE/FALSE |
| ISERROR | Test if cell value is an error. TRUE/FALSE |
| ISEVEN | Test if cell value is even. TRUE/FALSE |
| ISLOGICAL | Test if cell is logical (TRUE or FALSE). TRUE/FALSE |
| ISNA | Test if cell value is #N/A. TRUE/FALSE |
| ISNONTEXT | Test if cell is not text (blank cells are not text). TRUE/FALSE |
| ISNUMBER | Test if cell is a number. TRUE/FALSE |
| ISODD | Test if cell value is odd. TRUE/FALSE |
| ISTEXT | Test if cell is text. TRUE/FALSE |
| TYPE | Returns the type of value in a cell. |
| Math | |
| ABS | Calculates the absolute value of a number. |
| AGGREGATE | Define and perform calculations for a database or a list. |
| CEILING | Rounds a number up, to the nearest specified multiple. |
| COS | Returns the cosine of an angle. |
| DEGREES | Converts radians to degrees. |
| DSUM | Sums database records that meet certain criteria. |
| EVEN | Rounds to the nearest even integer. |
| EXP | Calculates the exponential value for a given number. |
| FACT | Returns the factorial. |
| FLOOR | Rounds a number down, to the nearest specified multiple. |
| GCD | Returns the greatest common divisor. |
| INT | Rounds a number down to the nearest integer. |
| LCM | Returns the least common multiple. |
| LN | Returns the natural logarithm of a number. |
| LOG | Returns the logarithm of a number to a specified base. |
| LOG10 | Returns the base-10 logarithm of a number. |
| MROUND | Rounds a number to a specified multiple. |
| ODD | Rounds to the nearest odd integer. |
| PI | The value of PI. |
| POWER | Calculates a number raised to a power. |
| PRODUCT | Multiplies an array of numbers. |
| QUOTIENT | Returns the integer result of division. |
| RADIANS | Converts an angle into radians. |
| RANDBETWEEN | Calculates a random number between two numbers. |
| ROUND | Rounds a number to a specified number of digits. |
| ROUNDDOWN | Rounds a number down (towards zero). |
| ROUNDUP | Rounds a number up (away from zero). |
| SIN | Returns the sine of an angle. |
| SUBTOTAL | Returns a summary statistic for a series of data. |
| SUM | Adds numbers together. |
| SUMIF | Sums numbers that meet a criteria. |
| SUMIFS | Sums numbers that meet multiple criteria. |
| SUMPRODUCT | Multiplies arrays of numbers and sums the resultant array. |
| TAN | Returns the tangent of an angle. |
| Stats | |
| AVERAGE | Averages numbers. |
| AVERAGEIF | Averages numbers that meet a criteria. |
| AVERAGEIFS | Averages numbers that meet multiple criteria. |
| CORREL | Calculates the correlation of two series. |
| COUNT | Counts cells that contain a number. |
| COUNTA | Count cells that are non-blank. |
| COUNTBLANK | Counts cells that are blank. |
| COUNTIF | Counts cells that meet a criteria. |
| COUNTIFS | Counts cells that meet multiple criteria. |
| FORECAST | Predict future y-values from linear trend line. |
| FREQUENCY | Counts values that fall within specified ranges. |
| GROWTH | Calculates Y values based on exponential growth. |
| INTERCEPT | Calculates the Y intercept for a best-fit line. |
| LARGE | Returns the kth largest value. |
| LINEST | Returns statistics about a trendline. |
| MAX | Returns the largest number. |
| MEDIAN | Returns the median number. |
| MIN | Returns the smallest number. |
| MODE | Returns the most common number. |
| PERCENTILE | Returns the kth percentile. |
| PERCENTILE.INC | Returns the kth percentile. Where k is inclusive. |
| PERCENTILE.EXC | Returns the kth percentile. Where k is exclusive. |
| QUARTILE | Returns the specified quartile value. |
| QUARTILE.INC | Returns the specified quartile value. Inclusive. |
| QUARTILE.EXC | Returns the specified quartile value. Exclusive. |
| RANK | Rank of a number within a series. |
| RANK.AVG | Rank of a number within a series. Averages. |
| RANK.EQ | Rank of a number within a series. Top Rank. |
| SLOPE | Calculates the slope from linear regression. |
| SMALL | Returns the kth smallest value. |
| STDEV | Calculates the standard deviation. |
| STDEV.P | Calculates the SD of an entire population. |
| STDEV.S | Calculates the SD of a sample. |
| STDEVP | Calculates the SD of an entire population |
| TREND | Calculates Y values based on a trendline. |
| Text | |
| CLEAN | Removes all non-printable characters. |
| DOLLAR | Converts a number to text in currency format. |
| FIND | Locates position of text within a cell.Case-sensitive. |
| LEFT | Truncates text a number of characters from the left. |
| LEN | Counts number of characters in text. |
| MID | Extracts text from the middle of a cell. |
| PROPER | Converts text to proper case. |
| REPLACE | Replaces text based on it's location. |
| REPT | Repeats text a number of times. |
| RIGHT | Truncates text a number of characters from the right. |
| SEARCH | Locates position of text within a cell.Not Case-sensitive. |
| SUBSTITUTE | Finds and replaces text. Case-sensitive. |
| TEXT | Converts a value into text with a specific number format. |
| TRIM | Removes all extra spaces from text. |