VBA – Arbeitsblattfunktionen verwenden (und eine volle Liste)
In this Article
Es gibt viele Möglichkeiten, Funktionen in VBA zu verwenden. VBA kommt mit vielen eingebauten Funktionen. Sie können sogar Ihre eigenen Funktionen (BDFs) erstellen. Sie können jedoch auch viele der Excel-Funktionen in VBA nutzen, indem Sie Application.WorksheetFunction verwenden.
Arbeitsblattfunktionen in VBA verwenden
Um auf eine Excel-Funktion in VBA zuzugreifen, fügen Sie Application.WorksheetFunction vor der Funktion ein, die Sie aufrufen möchten. Im folgenden Beispiel rufen wir die Excel-Funktion MAX auf:
Dim maxWert as long
maxWert = Application.WorksheetFunction.Max(Range("a1").Value, Range("a2").Value)Die Syntax der Funktionen ist dieselbe, allerdings geben Sie die Funktionsargumente genauso wie bei jeder anderen VBA-Funktion ein.
Beachten Sie, dass die Syntax der Max-Funktion bei der Eingabe erscheint (ähnlich wie bei VBA-Funktionen):
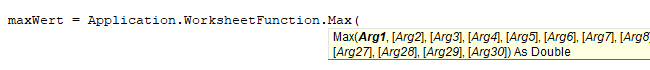
Die WorksheetFunction-Methode
WorksheetFunction ist eine Methode des Application-Objekts. Sie ermöglicht Ihnen den Zugriff auf viele (nicht alle) der standardmäßigen Excel-Arbeitsblattfunktionen. Im Allgemeinen erhalten Sie keinen Zugriff auf Arbeitsblattfunktionen, die eine entsprechende VBA-Version haben.
Nachstehend finden Sie eine Liste der gängigsten Arbeitsblattfunktionen.
Application.WorksheetFunction im Vergleich zu Application
Es gibt eigentlich zwei Möglichkeiten, auf diese Funktionen zuzugreifen:
Application.WorksheetFunction (wie oben gesehen):
maxWert = Application.WorksheetFunction.Max(Range("a1").Value, Range("a2").Value)oder Sie können die WorksheetFunction weglassen
maxWert = Application.Max(Range("a1").Value, Range("a2").Value)Leider wird durch das Weglassen von WorksheetFunction die IntelliSense-Funktion, die die Syntax anzeigt, ausgeschaltet (siehe Abbildung oben). Es hat jedoch einen großen potenziellen Vorteil: Die Fehlerbehandlung.
Wenn Sie Application verwenden und Ihre Funktion einen Fehler erzeugt, gibt sie den Fehlerwert zurück. Wenn Sie die WorksheetFunction-Methode verwenden, löst VBA einen Laufzeitfehler aus. Natürlich können Sie den VBA-Fehler behandeln, aber es ist normalerweise besser, den Fehler von vornherein zu vermeiden.
Schauen wir uns ein Beispiel an, um den Unterschied zu sehen:
Die Vlookup-Arbeitsblattfunktion – Fehlerbehandlung
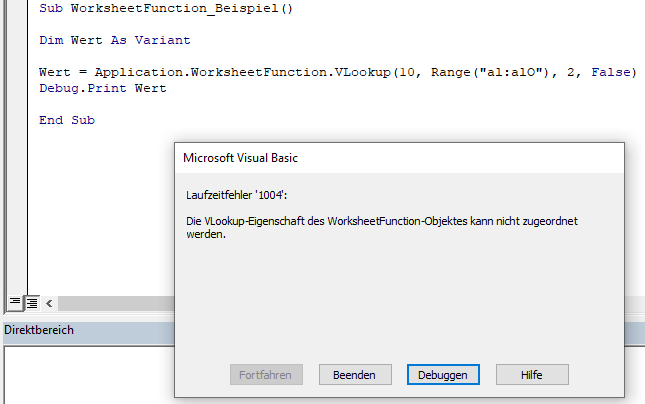
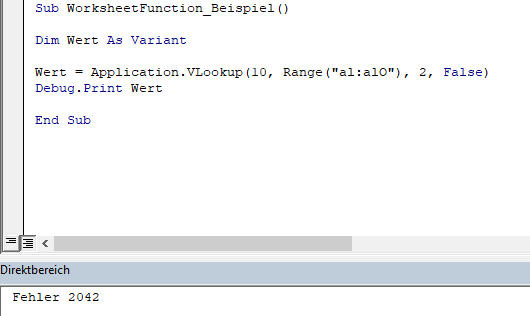
Wir werden versuchen, ein Vlookup (Deutsch: SVERWEIS) durchzuführen, das keine Übereinstimmung ergibt. Daher wird die Vlookup-Funktion einen Fehler zurückgeben.
Zunächst werden wir die WorksheetFunction-Methode verwenden. Beachten Sie, wie VBA einen Fehler auslöst:
Als nächstes lassen wir WorksheetFunction weg. Beachten Sie, dass kein Fehler ausgelöst wird und stattdessen die Variable „Wert“ den Fehlerwert aus dem Vlookup enthält.
Hinweis: Die Arbeitsblattfunktionen können nur unter Verwendung ihrer englischen Namen in VBA aufgerufen werden.
VBA-Arbeitsblattfunktionen Liste
Nachfolgend finden Sie eine Liste gängigster VBA-Arbeitsblattfunktionen.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Logical | |
| AND | Checks whether all conditions are met. TRUE/FALSE |
| IF | If condition is met, do something, if not, do something else. |
| IFERROR | If result is an error then do something else. |
| OR | Checks whether any conditions are met. TRUE/FALSE |
| Lookup & Reference | |
| CHOOSE | Chooses a value from a list based on it's position number. |
| HLOOKUP | Lookup a value in the first row and return a value. |
| INDEX | Returns a value based on it's column and row numbers. |
| LOOKUP | Looks up values either horizontally or vertically. |
| MATCH | Searches for a value in a list and returns its position. |
| TRANSPOSE | Flips the oriention of a range of cells. |
| VLOOKUP | Lookup a value in the first column and return a value. |
| Date & Time | |
| DATE | Returns a date from year, month, and day. |
| DATEVALUE | Converts a date stored as text into a valid date |
| DAY | Returns the day as a number (1-31). |
| DAYS360 | Returns days between 2 dates in a 360 day year. |
| EDATE | Returns a date, n months away from a start date. |
| EOMONTH | Returns the last day of the month, n months away date. |
| HOUR | Returns the hour as a number (0-23). |
| MINUTE | Returns the minute as a number (0-59). |
| MONTH | Returns the month as a number (1-12). |
| NETWORKDAYS | Number of working days between 2 dates. |
| NETWORKDAYS.INTL | Working days between 2 dates, custom weekends. |
| NOW | Returns the current date and time. |
| SECOND | Returns the second as a number (0-59) |
| TIME | Returns the time from a hour, minute, and second. |
| TIMEVALUE | Converts a time stored as text into a valid time. |
| WEEKDAY | Returns the day of the week as a number (1-7). |
| WEEKNUM | Returns the week number in a year (1-52). |
| WORKDAY | The date n working days from a date. |
| YEAR | Returns the year. |
| YEARFRAC | Returns the fraction of a year between 2 dates. |
| Engineering | |
| CONVERT | Convert number from one unit to another. |
| Financial | |
| FV | Calculates the future value. |
| PV | Calculates the present value. |
| NPER | Calculates the total number of payment periods. |
| PMT | Calculates the payment amount. |
| RATE | Calculates the interest Rate. |
| NPV | Calculates the net present value. |
| IRR | The internal rate of return for a set of periodic CFs. |
| XIRR | The internal rate of return for a set of non-periodic CFs. |
| PRICE | Calculates the price of a bond. |
| INTRATE | The interest rate of a fully invested security. |
| Information | |
| ISERR | Test if cell value is an error, ignores #N/A. TRUE/FALSE |
| ISERROR | Test if cell value is an error. TRUE/FALSE |
| ISEVEN | Test if cell value is even. TRUE/FALSE |
| ISLOGICAL | Test if cell is logical (TRUE or FALSE). TRUE/FALSE |
| ISNA | Test if cell value is #N/A. TRUE/FALSE |
| ISNONTEXT | Test if cell is not text (blank cells are not text). TRUE/FALSE |
| ISNUMBER | Test if cell is a number. TRUE/FALSE |
| ISODD | Test if cell value is odd. TRUE/FALSE |
| ISTEXT | Test if cell is text. TRUE/FALSE |
| TYPE | Returns the type of value in a cell. |
| Math | |
| ABS | Calculates the absolute value of a number. |
| AGGREGATE | Define and perform calculations for a database or a list. |
| CEILING | Rounds a number up, to the nearest specified multiple. |
| COS | Returns the cosine of an angle. |
| DEGREES | Converts radians to degrees. |
| DSUM | Sums database records that meet certain criteria. |
| EVEN | Rounds to the nearest even integer. |
| EXP | Calculates the exponential value for a given number. |
| FACT | Returns the factorial. |
| FLOOR | Rounds a number down, to the nearest specified multiple. |
| GCD | Returns the greatest common divisor. |
| INT | Rounds a number down to the nearest integer. |
| LCM | Returns the least common multiple. |
| LN | Returns the natural logarithm of a number. |
| LOG | Returns the logarithm of a number to a specified base. |
| LOG10 | Returns the base-10 logarithm of a number. |
| MROUND | Rounds a number to a specified multiple. |
| ODD | Rounds to the nearest odd integer. |
| PI | The value of PI. |
| POWER | Calculates a number raised to a power. |
| PRODUCT | Multiplies an array of numbers. |
| QUOTIENT | Returns the integer result of division. |
| RADIANS | Converts an angle into radians. |
| RANDBETWEEN | Calculates a random number between two numbers. |
| ROUND | Rounds a number to a specified number of digits. |
| ROUNDDOWN | Rounds a number down (towards zero). |
| ROUNDUP | Rounds a number up (away from zero). |
| SIN | Returns the sine of an angle. |
| SUBTOTAL | Returns a summary statistic for a series of data. |
| SUM | Adds numbers together. |
| SUMIF | Sums numbers that meet a criteria. |
| SUMIFS | Sums numbers that meet multiple criteria. |
| SUMPRODUCT | Multiplies arrays of numbers and sums the resultant array. |
| TAN | Returns the tangent of an angle. |
| Stats | |
| AVERAGE | Averages numbers. |
| AVERAGEIF | Averages numbers that meet a criteria. |
| AVERAGEIFS | Averages numbers that meet multiple criteria. |
| CORREL | Calculates the correlation of two series. |
| COUNT | Counts cells that contain a number. |
| COUNTA | Count cells that are non-blank. |
| COUNTBLANK | Counts cells that are blank. |
| COUNTIF | Counts cells that meet a criteria. |
| COUNTIFS | Counts cells that meet multiple criteria. |
| FORECAST | Predict future y-values from linear trend line. |
| FREQUENCY | Counts values that fall within specified ranges. |
| GROWTH | Calculates Y values based on exponential growth. |
| INTERCEPT | Calculates the Y intercept for a best-fit line. |
| LARGE | Returns the kth largest value. |
| LINEST | Returns statistics about a trendline. |
| MAX | Returns the largest number. |
| MEDIAN | Returns the median number. |
| MIN | Returns the smallest number. |
| MODE | Returns the most common number. |
| PERCENTILE | Returns the kth percentile. |
| PERCENTILE.INC | Returns the kth percentile. Where k is inclusive. |
| PERCENTILE.EXC | Returns the kth percentile. Where k is exclusive. |
| QUARTILE | Returns the specified quartile value. |
| QUARTILE.INC | Returns the specified quartile value. Inclusive. |
| QUARTILE.EXC | Returns the specified quartile value. Exclusive. |
| RANK | Rank of a number within a series. |
| RANK.AVG | Rank of a number within a series. Averages. |
| RANK.EQ | Rank of a number within a series. Top Rank. |
| SLOPE | Calculates the slope from linear regression. |
| SMALL | Returns the kth smallest value. |
| STDEV | Calculates the standard deviation. |
| STDEV.P | Calculates the SD of an entire population. |
| STDEV.S | Calculates the SD of a sample. |
| STDEVP | Calculates the SD of an entire population |
| TREND | Calculates Y values based on a trendline. |
| Text | |
| CLEAN | Removes all non-printable characters. |
| DOLLAR | Converts a number to text in currency format. |
| FIND | Locates position of text within a cell.Case-sensitive. |
| LEFT | Truncates text a number of characters from the left. |
| LEN | Counts number of characters in text. |
| MID | Extracts text from the middle of a cell. |
| PROPER | Converts text to proper case. |
| REPLACE | Replaces text based on it's location. |
| REPT | Repeats text a number of times. |
| RIGHT | Truncates text a number of characters from the right. |
| SEARCH | Locates position of text within a cell.Not Case-sensitive. |
| SUBSTITUTE | Finds and replaces text. Case-sensitive. |
| TEXT | Converts a value into text with a specific number format. |
| TRIM | Removes all extra spaces from text. |