Access VBA Recordsets – Open, Count, Loop and More
Written by
Reviewed by
In this Article
In this tutorial, we will learn how to open a Recordset, count the number of records in the Recordset, loop through the Recordset, add a record, update a record, read a value from a record, and delete a record.
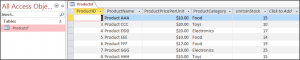
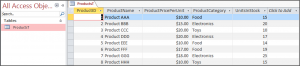
We have an Access Table, called ProductsT shown below:
Opening a Recordset
We first need to establish the database we intend to use, in this case it is the currently opened database. We can then use the CurrentDB.OpenRecordSet method to open/create our Recordset.
In order to create a Recordset that will allow us to manipulate the data in the table called ProductsT, we would use the following code:
CurrentDb.OpenRecordset ("ProductsT")Counting the number of Records using VBA
Once you have created a Recordset, you would more than likely want to do something useful with it or manipulate the data in it in some way. You can count the number of records in your dataset (in this case the table called ProductsT) using the following code:
MsgBox CurrentDb.OpenRecordset("ProductsT").RecordCount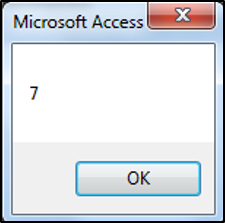
Looping through a RecordSet using VBA
The following code loops through our RecordSet:
Sub RecordSet_Loop ()
Dim ourDatabase As Database
Dim ourRecordset As Recordset
Set ourDatabase = CurrentDb
Set ourRecordset = ourDatabase.OpenRecordset("ProductsT")
Do Until ourRecordset.EOF
MsgBox ourRecordset!ProductID
ourRecordset.MoveNext
Loop
End SubAdding a record to a RecordSet
Use the Recordset.AddNew method to add a new record to the RecordSet:
Sub RecordSet_Add()
With CurrentDb.OpenRecordset("ProductsT")
.AddNew
![ProductID] = 8
![ProductName] = "Product HHH"
![ProductPricePerUnit] = 10
![ProductCategory] = "Toys"
![UnitsInStock] = 15
.Update
End With
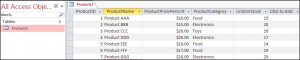
End SubThe result is:
Updating a Recordset
You have to use the Recordset.AddNew or Recordset.Edit method. After this statement you must use the Recordset.Update method in order to keep the changes.
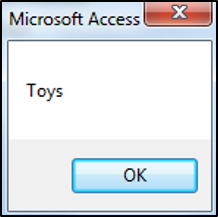
Reading Values from a Record
You have to use the Recordset.FindFirst method to make a record, the current record. You then have to use Recordset.Fields to specify which field to look at.
Sub RecordSet_ReadValue ()
Dim ourDatabase As Database
Dim ourRecordset As Recordset
Set ourDatabase = CurrentDb
Set ourRecordset = ourDatabase.OpenRecordset("ProductsT", Type:=RecordsetTypeEnum.dbOpenDynaset)
With ourRecordset
.FindFirst "ProductName = " & "'Product CCC'"
If .NoMatch Then
MsgBox "No Match Found"
Else
MsgBox ourRecordset.Fields("ProductCategory")
End If
End With
End SubThe result is:
Deleting a Record from a Recordset
In order to delete a record from a Recordset you have to first make it the current record using the Recordset.FindFirst method. You can then delete it using the Recordset.Delete method. The following code shows how to delete record 2 in the data set:
Sub RecordSet_DeleteRecord ()
Dim ourDatabase As Database
Dim ourRecordset As Recordset
Set ourDatabase = CurrentDb
Set ourRecordset = ourDatabase.OpenRecordset("ProductsT", Type:=RecordsetTypeEnum.dbOpenDynaset)
With ourRecordset
.FindFirst "ProductName = " & "'Product BBB'"
If .NoMatch Then
MsgBox "No Match Found"
Else
ourRecordset.Delete
End If
End With
'Re-open Table
DoCmd.Close acTable, "ProductsT"
DoCmd.OpenTable "ProductsT"
End SubThe result is: