VBA Cheat Sheets – Commands & Syntax Lists
Last updated on July 19, 2021
.
VBA Cheat Sheet PDF (Free Download) Download our free Excel VBA Cheat Sheet PDF for quick reference!
Download
VBA Cheat Sheets Reference this page for lists of all common VBA Commands & Syntax. You will find many basic commands (ex. insert a sheet) and some advanced syntax (ex. working with arrays).
Tips:
Use CTRL + F to search this page.
Bookmark this page (CTRL + D on Chrome)!
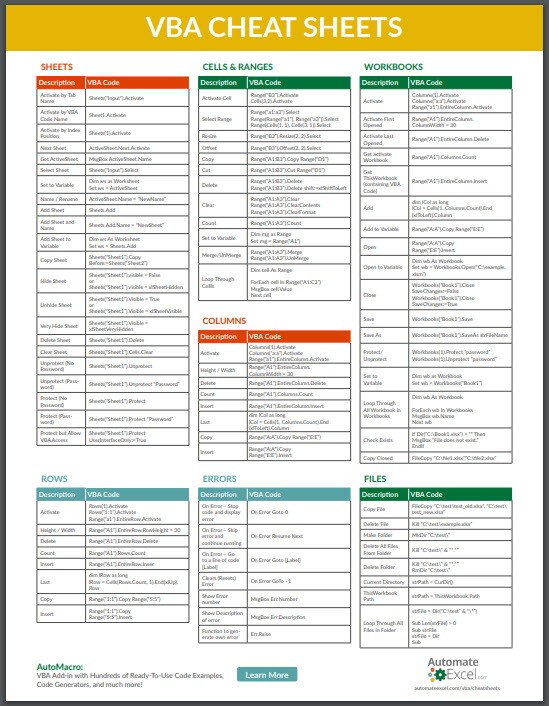
Sheets
Activate by Tab Name
Sheets(“Input”).Activate
Activate by VBA Code Name
Sheet1.Activate
Activate by Index Position
Sheets(1).Activate
Next Sheet
ActiveSheet.Next.Activate
Get ActiveSheet
MsgBox ActiveSheet.Name
Select Sheet
Sheets(“Input”).Select
Set to Variable
Dim ws as WorksheetSet ws = ActiveSheet
Name / Rename
ActiveSheet.Name = “NewName”
Add Sheet and Name
Sheets.Add.Name = “NewSheet”
Add Sheet to Variable
Dim ws As WorksheetSet ws = Sheets.Add
Copy Sheet
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Copy Before:=Sheets(“Sheet2”)
Hide Sheet
Sheets(“Sheet1”).visible = False
Unhide Sheet
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Visible = True
Very Hide Sheet
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Visible = xlSheetVeryHidden
Delete Sheet
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Delete
Clear Sheet
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Cells.Clear
Unprotect (No Password)
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Unprotect
Unprotect (Password)
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Unprotect “Password”
Protect (No Password)
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Protect
Protect (Password)
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Protect “Password”
Protect but Allow VBA Access
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Protect UserInterfaceOnly:=True
Return to Top
Cells & Ranges
Activate Cell
Range(“B3”).Activate
Select Range
Range(“a1:a3”).Select
Resize
Range(“B3”).Resize(2, 2).Select
Offset
Range(“B3”).Offset(2, 2).Select
Copy
Range(“A1:B3”).Copy Range(“D1”)
Cut
Range(“A1:B3”).Cut Range(“D1”)
Delete
Range(“A1:B3”).Delete
Clear
Range(“A1:A3”).Clear
Count
Range(“A1:A3”).Count
Set to Variable
Dim rng as RangeSet rng = Range(“A1”)
Merge/UnMerge
Range(“A1:A3”).Merge
Loop Through Cellls
Dim cell As Range
For Each cell In Range(“A1:C3”)Next cell
Return to Top
Rows
Activate
Rows(1).Activate
Height / Width
Range(“A1”).EntireRow.RowHeight = 30
Delete
Range(“A1”).EntireRow.Delete
Count
Range(“A1”).Rows.Count
Insert
Range(“A1”).EntireRow.Insert
Last
dim lRow as long
Copy
Range(“1:1”).Copy Range(“5:5”)
Insert
Range(“1:1”).Copy
Return to Top
Columns
Activate
Columns(1).Activate
Height / Width
Range(“A1”).EntireColumn.ColumnWidth = 30
Delete
Range(“A1”).EntireColumn.Delete
Count
Range(“A1”).Columns.Count
Insert
Range(“A1”).EntireColumn.Insert
Last
dim lCol as long
Copy
Range(“A:A”).Copy Range(“E:E”)
Insert
Range(“A:A”).Copy
Return to Top
Workbooks
Activate
Workbooks(“Book1”).Activate
Activate First Opened
Workbooks(1).Activate
Activate Last Opened
Workbooks(Workbooks.Count).Activate
Get ActivateWorkbook
MsgBox ActiveWorkbook.Name
Get ThisWorkbook (containing VBA Code)
MsgBox ThisWorkbook.Name
Add to Variable
Dim wb As WorkbookSet wb = Workbooks.Add
Open
Workbooks.Open(“C:\example.xlsm”)
Open to Variable
Dim wb As WorkbookSet wb = Workbooks.Open(“C:\example.xlsm”)
Close
Workbooks(“Book1”).Close SaveChanges:=False :=True
Save
Workbooks(“Book1”).Save
Save As
Workbooks(“Book1”).SaveAs strFileName
Protect/Unprotect
Workbooks(1).Protect “password”
Set to Variable
Dim wb as WorkbookSet wb = Workbooks(“Book1”)
Loop Through All Workbook in Workbooks
Dim wb As Workbook
For Each wb In WorkbooksNext wb
Check Exists
If Dir(“C:\Book1.xlsx”) = “” Then
Copy Closed
FileCopy “C:\file1.xlsx”,”C:\file2.xlsx”
Return to Top
Settings
Screen Updating
Application.ScreenUpdating = False = True
Display Alerts
Application.DisplayAlerts = False = True
Events
Application.EnableEvents = False = True
Enable Cancel Key
Application.EnableCancelKey = xlDisabled
Text Compare – Ignore Case
Option Compare Text
Require Variable Declaration
Option Explicit
Automatic Calculations
Application.Calculation = xlManual
Background Error Checking
Application.ErrorCheckingOptions.BackgroundChecking = False = True
Display Formula Bar
Application.DisplayFormulaBar = False = True
Freeze Panes
ActiveWindow.FreezePanes = False = True
Full Screen View
Application.DisplayFullScreen = False = True
PageBreak Preview
ActiveWindow.View = xlPageBreakPreview
Display Scroll Bars
With ActiveWindow= False = False End With With ActiveWindow= True = True End With
Display Status Bar
Application.DisplayStatusBar = False = True
Status Bar Contents
Application.StatusBar = “I’m working Now!!!”= False
Display Workbook Tabs
ActiveWindow.DisplayWorkbookTabs = False = True
UserName
Application.UserName = “AutomateExcel.com”
App Caption
Application.Caption = “AutomateExcel Model”
Zoom
ActiveWindow.Zoom = 80
Return to Top
Errors
On Error – Stop code and display error
On Error Goto 0
On Error – Skip error and continue running
On Error Resume Next
On Error – Go to a line of code [Label]
On Error Goto [Label]
Clears (Resets) Error
On Error GoTo –
Show Error number
MsgBox Err.Number
Show Description of error
MsgBox Err.Description
Function to generate own error
Err.Raise
Return to Top
Files
Copy File
FileCopy “C:\test\test_old.xlsx”, “C:\test\test_new.xlsx”
Delete File
Kill “C:\test\example.xlsx”
Make Folder
MkDir “C:\test\”
Delete All Files From Folder
Kill “C:\test\” & “*.*”
Delete Folder
Kill “C:\test\” & “*.*”
Current Directory
strPath = CurDir()
ThisWorkbook Path
strPath = ThisWorkbook.Path
Loop Through All Files in Folder
strFile = Dir(“C:\test” & “\*”)
Do While Len(strFile) > 0Debug.Print strFileLoop
Return to Top
Arrays
Create
Dim arr(1 To 3) As Variant
Create From Excel
Dim arr(1 To 3) As VariantDim cell As Range, i As Integer In Range(“A1:A3”)Next cell
Read All Items
Dim i as LongFor i = LBound(arr) To UBound(arr)Next i
Array to String
Dim sName As String
Increase Size
ReDim Preserve arr(0 To 100)
Return to Top
Collections
Create
Dim coll As New Collection
Create From Excel
Dim coll As New CollectionDim cell As Range In Range(“A1:A2”)Next cell
Add Item
coll.Add “Value”
Add Item Before
coll.Add “Value”, Before:=1
Add Item After
coll.Add “Value”, After:=1
Read Item
MsgBox coll (1)
Read All Items
Dim item As VariantFor Each item In collNext item
Remove Item
coll.Remove (1)
Remove All Items
Set coll = New Collection
Return to Top
Dictionaries
Required Reference
Tools > References > Microsoft Scripting Runtime
Create
Dim dict As New Scripting.Dictionary
Create From Excel
Dim dict As New Scripting.DictionaryDim cell As RangeDim key As Integer In Range(“A1:A10”)Next cell
Add Item
dict.Add “Key”, “Value”
Change Value
dict(“Key”) = “Value”
Get Value
MsgBox dict(“Key”)
Check For Value
If dict.Exists(“Key”) Then End If
Remove Item
dict.Remove (“Key”)
Remove All Items
dict.RemoveAll
Loop Through Items
Dim key As VariantFor Each key In dict.KeysNext key
Make Key Case Sensitive
dict.CompareMode = vbBinaryCompare
Make Key Case Insensitive
dict.CompareMode = vbTextCompare
Return to Top
AutoMacro – The Ultimate VBA Add-in
AutoMacro: VBA Add-in with Hundreds of Ready-To-Use VBA Code Examples & much more!
Learn More