VBA Multi-Dimensional Array (2D Arrays)
Written by
Reviewed by
In this Article
This tutorial will discuss 2-d and multi-dimensional arrays in VBA.
Multi-Dimensional Array (2D Arrays)
Multi-dimensional Arrays are arrays that contain more than one dimension, usually two or three dimensions, but arrays can have up to 32 dimensions.
Declare a 2D Array
To create an array with more than one dimension, use commas to define each separate dimension:
Dim intArr(2,3) as IntegerPopulating a 2D Array
The code below will populate a 2D array, and then populate the rows and columns of a worksheet with the values in the array.
Sub Populate2D()
'declare the 2D array
Dim intA(2, 3) As Integer
'declare variables
Dim rw As Integer
Dim col As Integer
'populate the array
intA(0, 0) = 45
intA(0, 1) = 50
intA(0, 2) = 55
intA(0, 3) = 60
intA(1, 0) = 65
intA(1, 1) = 70
intA(1, 2) = 75
intA(1, 3) = 80
intA(2, 0) = 85
intA(2, 1) = 90
intA(2, 2) = 95
intA(2, 3) = 100
'loop through the array and populate Excel
For rw = 0 To 2
For col = 0 To 3
Cells(rw + 1, col + 1).Value = intA(rw, col)
Next col
Next rw
End SubYour Excel spreadsheet should then be populated as follows.
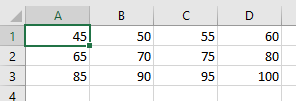
Populating a 2D Array from Excel data
The code below will populate a 2D array from an Excel worksheet and then populate a different sheet with the data.
Sub Populate2D()
'Declare the worksheets
Dim ws_Source As Worksheet
Dim ws_Destination As Worksheet
'Declare the array
Dim wsData(10, 2) As Variant
'Declare the variables
Dim rw as Integer
Dim col As Integer
'refer to the source sheet
Set ws_Source = Worksheets("Sheet1")
'get the information from the source sheet and populate the array
For rw = LBound(wsData, 1) To UBound(wsData, 1)
For col = LBound(wsData, 2) To UBound(wsData, 2)
wsData(rw, col) = ws_Source.Range("A2").Offset(rw, col).Value
Next col
Next rw
'refer to the destation sheet
Set ws_Destination = Worksheets("Sheet2")
' populate the destination sheet from the array
For rw = LBound(wsData, 1) To UBound(wsData, 1)
For col = LBound(wsData, 2) To UBound(wsData, 2)
ws_Destination.Range("A1").Offset(rw,col).Value = wsData(rw, col)
Next col
Next rw
End SubResizing using ReDim and Re-Dim Preserve
You can resize an array using ReDim (learn more).
Sub Resize2D()
'declare the array
Dim varArray() as Variant
'declare the size of the array
ReDim varArray(1, 2)
varArray(0, 0) = "Mel Smith"
varArray(0, 1) = "Fred Buckle"
varArray(0, 2) = "Jane Eyre"
varArray(1, 0) = "Accountant"
varArray(1, 1) = "Secretary"
varArray(1, 2) = "Doctor"
'redeclare the size of the array
ReDim varArray(0, 1)
'repopulate the array
varArray(0, 0) = "Mel Smith"
varArray(0, 1) = "Fred Buckle"
End SubWhen you redeclare the array, you will lose any data previously held in the array unless you use the ReDim Preserve Statement.
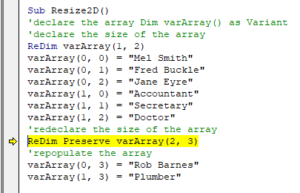
Sub Resize2D()
'declare the array
Dim varArray() as Variant
'declare the size of the array
ReDim varArray(1, 2)
varArray(0, 0) = "Mel Smith"
varArray(0, 1) = "Fred Buckle"
varArray(0, 2) = "Jane Eyre"
varArray(1, 0) = "Accountant"
varArray(1, 1) = "Secretary"
varArray(1, 2) = "Doctor"
'redeclare the size of the array
ReDim Preserve varArray(1, 3)
'populate the array with additional values
varArray(0, 3) = "Rob Barnes"
varArray(1, 3) = "Plumber"
End SubYou can only resize the last dimension of an Array if want to keep the original data in the Array with Re-Dim Preserve.
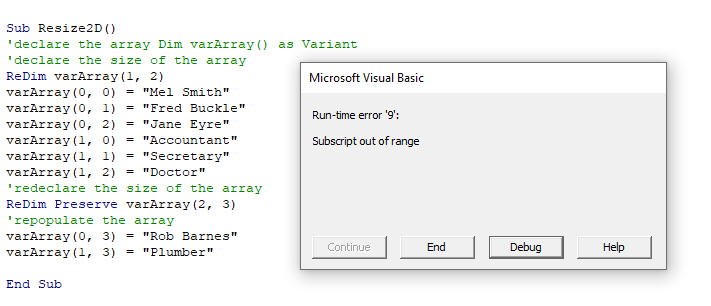
When you click debug, the error will be highlighted showing that the first dimension in the array is not the same as the first dimension when the array size was originally declared.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro - A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!